Collocation BEM for 3D Lame Equation
Download CBEM_LAM, a package for solving the 3D Lamé equation based on a piecewise constant Collocation Boundary Element Method, and employing a boundary-only discretization technique.
Piecewise constant collocation method
The displacement ![]() and traction
and traction ![]() are assumed to be constant over each boundary element. It can be shown (see e.g. [2]) that the elastic potentials
are assumed to be constant over each boundary element. It can be shown (see e.g. [2]) that the elastic potentials
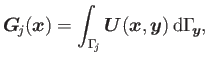 and
and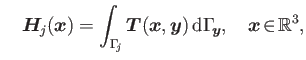
due to a uniform distribution over a flat triangle ![]() can be employed to successfully compute
can be employed to successfully compute ![]() and
and ![]() on
on ![]() . In addition, these potentials can be utilized to effectively calculate the displacement
. In addition, these potentials can be utilized to effectively calculate the displacement ![]() at interior points
at interior points ![]() The analytic expressions for
The analytic expressions for ![]() and
and ![]() over a flat triangle are given in [1]. Moreover, due to its boundary representation, the elastic Newton potential can also be effectively evaluated without the need of a volume-fitted mesh [2]. A brief description of the boundary-only discretization of the elastic Newton potential can be found in the user guide cbem_lamGuide.pdf provided in the package CBEM_LAM.
over a flat triangle are given in [1]. Moreover, due to its boundary representation, the elastic Newton potential can also be effectively evaluated without the need of a volume-fitted mesh [2]. A brief description of the boundary-only discretization of the elastic Newton potential can be found in the user guide cbem_lamGuide.pdf provided in the package CBEM_LAM.
References
- [1] S. Nintcheu Fata.
Explicit expressions for three-dimensional boundary integrals in linear elasticity.
J. Comput. Appl. Math., 235(15):4480-4495, 2011. - [2] S. Nintcheu Fata.
Boundary integral approximation of volume potentials in three-dimensional linear elasticity.
J. Comput. Appl. Math., 242(1):275-284, 2013.

